
If you’re a parent or caregiver of a child with autism, you’ve likely explored many therapies, interventions, and strategies to help your child thrive. Amidst this ocean of possibilities, one highly effective approach has been making waves: Parent-Child Interaction Therapy (PCIT).
But is it the right fit for your child with autism? Let’s dive in and explore how PCIT can make a difference in your family’s life.
However, first things first. What is Parent-Child Interaction Therapy (PCIT)?
Parent-Child Interaction Therapy (PCIT) is a proven, evidence-based treatment designed for young children who experience behavioral challenges. PCIT sessions are unique in that they involve real-time ‘coaching.’ During these sessions, you and your child are in a playroom while the therapist observes from another room, using either a one-way mirror or live video feed.
You’ll wear a ‘bug-in-the-ear’ device, which allows the therapist to provide immediate guidance as you learn new skills to effectively manage your child’s behavior. The beauty of PCIT lies in its focus on enhancing the parent-child bond through real-time coaching. Imagine wearing an earpiece while you interact with your child, with a therapist guiding you through those often tricky moments.
Sounds great, right? It’s highly effective, too!
PCIT is designed to improve the quality of the relationship between parents and their children while promoting positive behavioral changes. PCIT is typically recommended for children between the ages of 2 and 7 who face emotional and behavioral challenges. However, for young children on the autism spectrum, where communication difficulties are common, this intervention is transformative.
Why PCIT Works for Kids with Autism
PCIT works because it taps into one of the most powerful influences in a child’s life: you! Parents and caregivers are the constant presence in a child’s world, and by learning therapeutic techniques yourself, you become the agent of change.
For kids with autism, who often struggle with emotional regulation, social interaction, and understanding expectations, PCIT offers a structured way to address these areas. By improving communication between parent and child, the therapy allows children to feel more understood and safe.
One of the unique aspects of PCIT is the use of praise to shape positive behaviors. For children with ASD, who may struggle with motivation due to differences in how they process rewards, constant reinforcement can encourage them to engage more in their surroundings.
PCIT + Autism = Connection and Growth. Here’s why:
- Behavioral Improvements: Research shows that PCIT significantly reduces behavioral problems, such as aggression and tantrums, in children with autism. By using immediate feedback and structured techniques, you help your child understand social norms better.
- Social Skills: Children with autism often have difficulties with social cues. PCIT gives parents tools to help their child navigate these challenges, such as teaching them how to take turns, express needs, or follow instructions.
- Emotional Regulation: Children on the autism spectrum may experience heightened emotions or meltdowns. PCIT empowers parents with calming techniques that help manage those tough moments.
But Does PCIT Really Work? The Research Speaks
In short, yes! PCIT has been backed by numerous studies, showing significant improvements in children. A 2022 study found that children who participated in PCIT demonstrated notable reductions in problem behaviors and increases in compliance with parental requests.
Follow-up studies on PCIT also show that the benefits don’t just stop when the sessions end—they last! Research has found that positive changes in the parent-child relationship continue anywhere from 10 months to even 6 years after treatment (Hood & Eyberg, 2003; Boggs et al., 2004). Impressive, right?
For the kids, this means fewer disruptive behaviors (think tantrums and defiance) and more positive, meaningful interactions with their families. And the parents? They report feeling more confident in managing their child’s behavior, enjoying more positive moments with their kids, and feeling less stressed overall (Hood & Eyberg, 2003; Boggs et al., 2004).
It’s not just a quick fix—PCIT offers long-lasting benefits for the whole family! And while every child is different, the structured approach of PCIT offers tangible results for many families.
Is PCIT Right for Your Child?
Now, you’re probably wondering: Will PCIT work for my child?
The answer lies in understanding your child’s specific needs. PCIT is particularly helpful if your child struggles with:
- Communication barriers
- Behavioral issues like tantrums or aggression
- Difficulty following instructions
- Emotional regulation challenges
If you’re looking for a therapy that empowers you as a parent while directly supporting your child, PCIT is a strong contender. Plus, PCIT’s flexible, two-phase structure –Child-Directed Interaction and Parent-Directed Interaction– means it’s tailored to progress at your child’s pace.
Choosing the Right Support: Why Early Autism Ventures (EAV) is Your Best Bet
At Early Autism Services (EAV), we don’t just offer services; we build partnerships with families. Our approach is compassionate, evidence-based, and tailored specifically to each child’s unique needs. With a team of highly trained professionals, we’ll guide you through various proven therapies designed to help your child thrive.
Why should you choose EAV for your child’s special needs?
- Individualized Care: We understand that no two children with autism are the same, and that’s why we customize our services to meet your child’s needs.
- Expert Guidance: Our expert clinicians are leaders in the field, continually trained in the latest autism therapies like PCIT, Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA), and more.
- Parent Empowerment: We don’t just work with your child—we work with you. You’ll gain the skills and confidence to support your child both during and after therapy sessions.
- Success Stories: Families consistently see improvements, whether it’s reduced meltdowns, improved social interactions, or strengthened parent-child bonds.
Ready to Make a Difference in Your Child’s Life?
If you’re ready to see what we can do for your family, there’s no better time than now to take that first step. Early Autism Ventures is here to support you with a team that truly cares about your child’s success.
Contact EAV today for a free consultation and see how our services can transform your child’s life. Don’t wait—every moment is a chance to make meaningful progress!
Speak with a clinician today at +91 8929153820 or schedule a FREE consultation here.
Let’s build the future your child deserves, together.
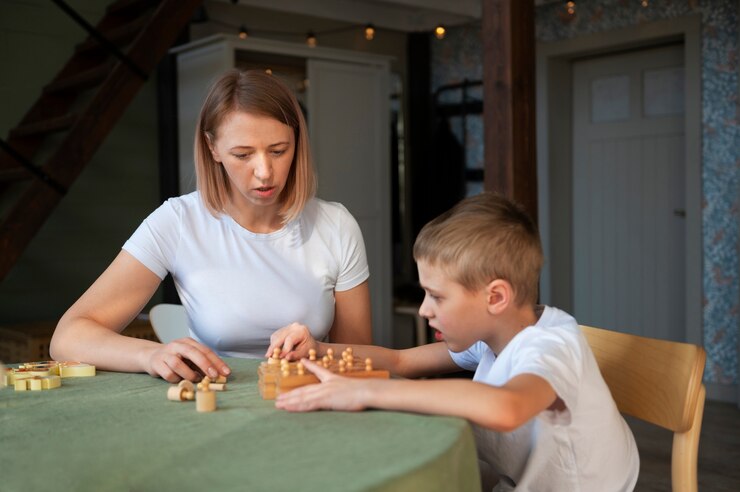
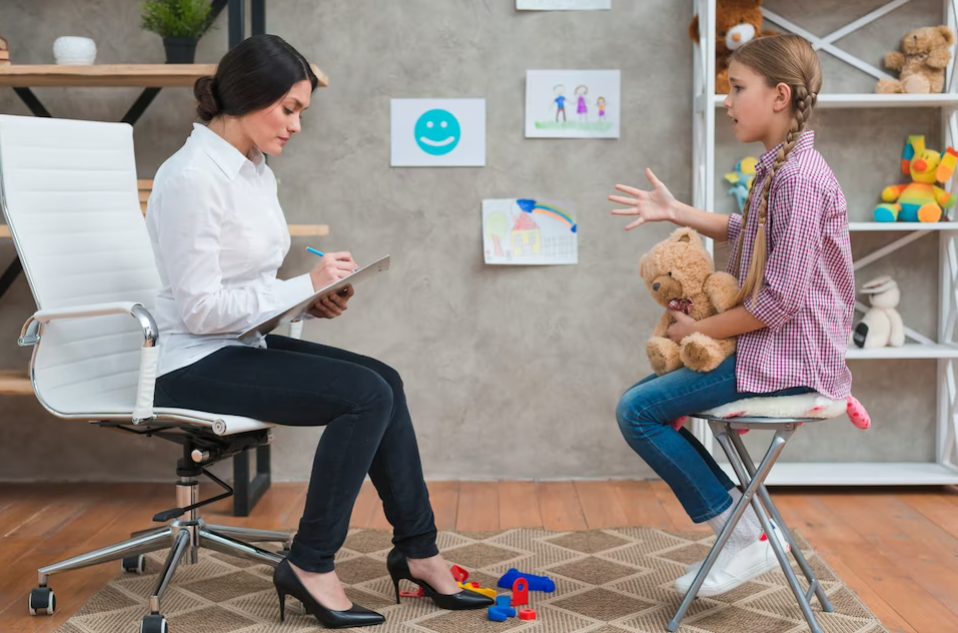















 During cognitive behavioural therapy sessions, your child works hand in hand with trained behaviour analysts, such as those at
During cognitive behavioural therapy sessions, your child works hand in hand with trained behaviour analysts, such as those at


















Recent Comments