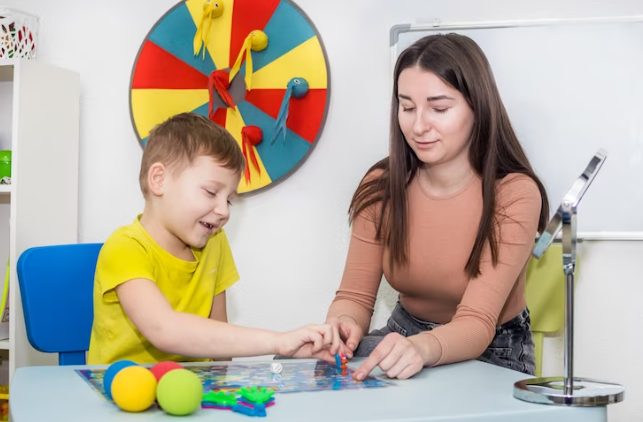

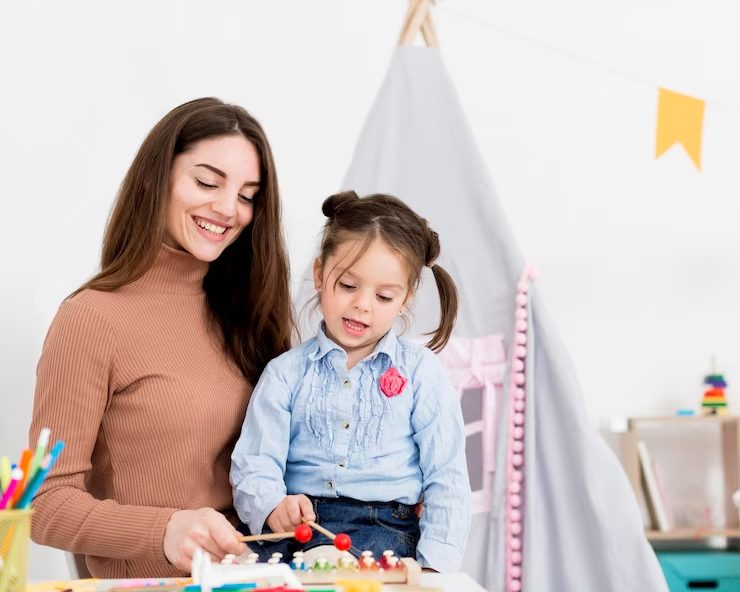
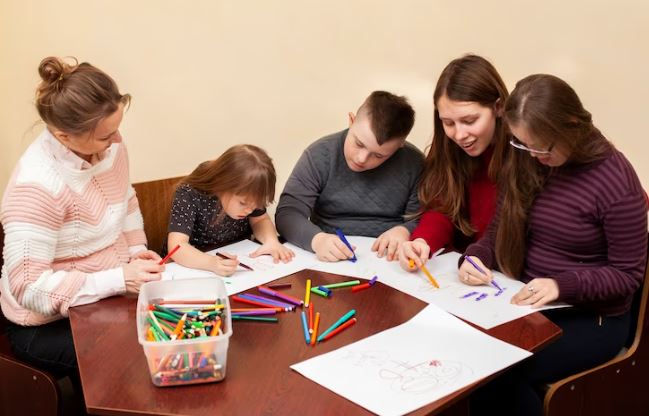
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) is a structured and evidence-based approach aimed at enhancing positive behaviors while reducing behaviors that may interfere with learning. It is a personalized, data-driven, and scientifically validated approach that helps address and understand the unique needs of children with autism.
While research consistently demonstrates its effectiveness in improving language and communication skills, as well as cognitive and adaptive functioning, ABA therapy also plays a vital role in reducing challenging behaviors. In turn, it makes daily life more manageable for children with ASD and their families. Moreover, the approach also fosters the development of essential life skills, including social interaction and self-care, empowering them for greater independence.
In this blog, we will explore the advantages of ABA therapy and understand why it’s essential to opt for ABA therapy classes near you.
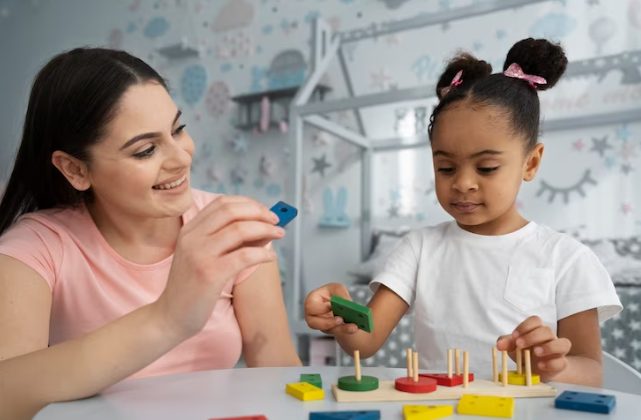
Individualized Approach
ABA therapy is renowned for its tailored approach, addressing the unique needs and abilities of each child. According to an article published in the Clinical Psychology Review, the field of applied behavior analysis has shown a more significant growth in the area of behavioral intervention for children with autism and autism spectrum disorders. These personalized interventions not only build confidence but also empower children to express themselves more effectively.
Life Skills Development
Another crucial facet of ABA therapy is its emphasis on essential life skills. It focuses on nurturing vital abilities like communication, social interaction, and self-care. These skills are pivotal for a child’s journey toward greater independence. A recent study underscores the significance of early intensive ABA therapy, highlighting significant gains in cognitive and adaptive functioning.
Reduction of Challenging Behaviours
Challenging behaviors can pose significant hurdles in the daily lives of children with autism and their families. ABA therapy offers effective strategies for addressing and mitigating these behaviors, thus enhancing overall family well-being. This reduction not only improves the child’s quality of life but also fosters a more harmonious family environment.
Encouraging Positive Social Interactions
One of the most essential aspects of ABA therapy is its role in nurturing positive social interactions and improved communication. ABA therapy provides children with autism the tools they need to form meaningful connections with peers and family members. Research published in Autism reinforces the idea that ABA therapy enhances social reciprocity and interaction among children on the autism spectrum. Through these transformative interventions, children can thrive and find their voice, which collectively contributes toward enhancing their overall quality of life.
Selecting ABA therapy classes close to you holds immense importance when it comes to the well-being and development of your child. This decision isn’t just about proximity; it’s about creating an environment that is conducive to optimal growth and support for your child on the autism spectrum. In the realm of autism therapy, choosing the right autism care provider in close proximity matters, and here’s why –
- Accessibility: Opting for ABA therapy close to where you live, whether it’s the same city or locality, ensures easy access, minimizing travel time and stress for both you and your child. This convenience also promotes regular attendance, which is vital for the effectiveness of therapy. Moreover, local ABA therapy providers, such as Early Autism Services (EAS), are often well-versed in the specific needs of your community, allowing them to tailor therapy programs to better suit your child’s unique requirements.
- Effective Communication: Proximity facilitates direct and efficient communication between you, the therapists, and the support team, ensuring that everyone is on the same page regarding your child’s development.
- Community Support: Being part of a local ABA therapy community provides opportunities for networking and mutual support with other parents who may be facing similar challenges. Sharing experiences and resources can be immensely helpfu! Besides, since ABA therapy requires consistency and routine, choosing therapy services nearby ensures that you and your little one can stick to a regular schedule, which is highly essential for progress.
- Familiar Environment: Your child may feel more comfortable and secure in a familiar environment. Local ABA therapy allows them to receive treatment in surroundings they know and trust. Additionally, these facilities often have established connections with local schools and educational institutions, making it easier to collaborate on your child’s educational plan.
In essence, choosing ABA therapy classes near you not only promotes convenience but also enables a holistic, community-oriented approach that can significantly benefit your child’s progress and overall well-being.
Partnering with Our Autism Care Services
The advantages of ABA therapy are backed by compelling statistics and, more importantly, by countless success stories from families like yours. And if you’re looking to embark on this transformative exploration of ASD support and care, we strongly encourage you to consider partnering with Early Autism Services (EAS).
At EAS, our dedicated team of experts, personalized programs, and unwavering commitment to your child’s well-being make us your trusted partner. Together, we can create a brighter future filled with possibilities and milestones for your child!
So, contact us today to explore ABA therapy classes near you and provide your child with the best chance for a brighter tomorrow.
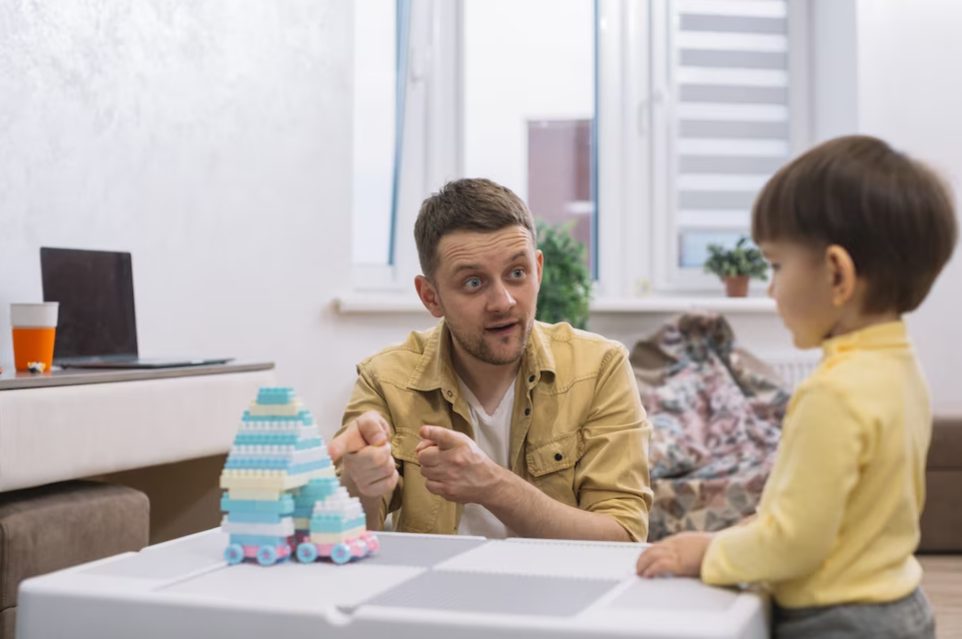
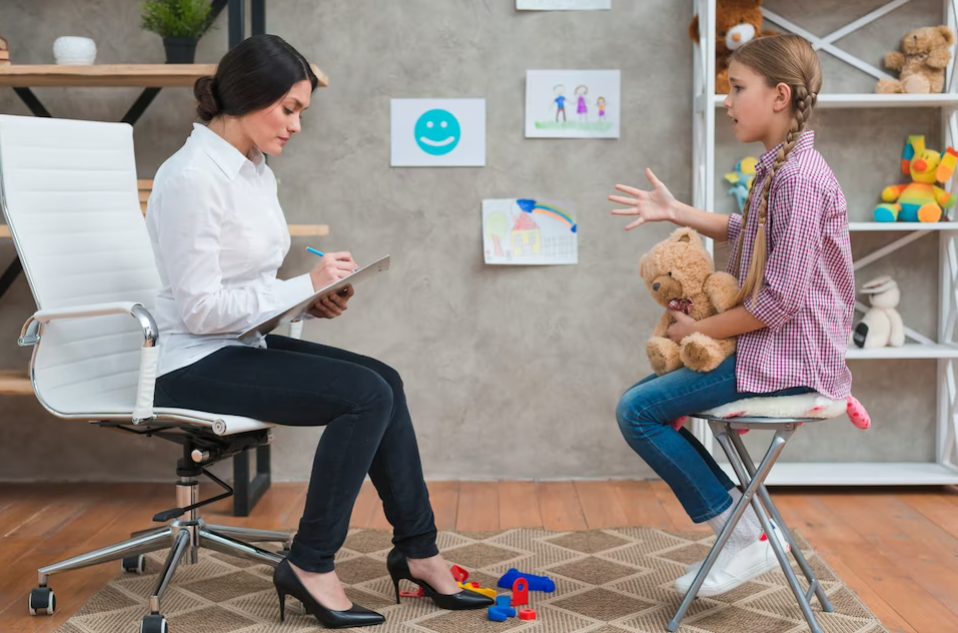

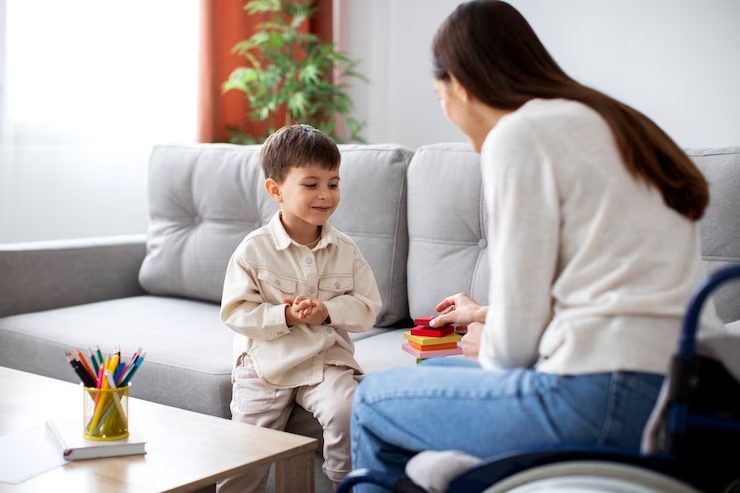
 During cognitive behavioural therapy sessions, your child works hand in hand with trained behaviour analysts, such as those at
During cognitive behavioural therapy sessions, your child works hand in hand with trained behaviour analysts, such as those at





























 A:
A:
Recent Comments