
When a child receives an autism diagnosis, parents and caregivers often find themselves flooded with questions: What causes autism? Can it be prevented? How can I support my child? One area of growing interest is genetic testing. Genetic research and testing have made significant strides in understanding autism, and many families are curious about what this means for them.
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a complex developmental condition with a wide range of behaviors, communication challenges, and social difficulties. While the exact cause of autism remains unknown, genetic factors play a significant role and understanding these factors can help caregivers better support their child’s unique needs.
But what does the research really say about the role of genetics in autism? How can genetic testing and therapies, like Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA), help?
Let’s dive into what the latest studies reveal, and how you can use this knowledge to benefit your child.
What Is Genetic Testing for Autism?
Genetic testing involves analyzing an individual’s DNA to look for specific changes or mutations. These changes, often referred to as variants, can offer insights into why a child may have developed autism or other conditions. For autism, several genes have been identified that may increase the likelihood of a diagnosis.
While there isn’t one “autism gene,” research has uncovered that autism can be linked to hundreds of different genes. According to a study, over 100 genes have been identified that could increase the risk of autism, with rare variants contributing significantly to more severe cases. Genetic testing can help identify these variants, providing some families with clarity and direction.
But it’s essential to remember that genetic testing is not diagnostic. It cannot predict whether your child will develop autism or how severe their symptoms might be. However, it can offer valuable information for creating a tailored care plan.
Personalized Intervention: Can Genetic Testing Guide Treatment for ASD?
Studies on families and heritability have shown that genetics play a significant role in autism, with estimates suggesting that up to 90% of autism risk may be genetic. However, conditions caused by single gene mutations, like Fragile X syndrome and Rett syndrome, only account for less than 10% of all autism cases. While these conditions are examples of rare genetic links to autism, most cases involve more complex interactions between many genes. (Source: Clinical Assessment, Genetics, and Treatment Approaches in Autism Spectrum Disorder)
While there is no “cure” for autism, genetic testing can assist in guiding treatment. In some cases, understanding a child’s genetic makeup can point parents toward specific therapies or medications that may be more effective.
This is where personalized intervention comes in. Personalized intervention uses a child’s unique genetic profile to determine which treatments are likely to work best for them, as per a 2023 study. It also explores how early intervention combined with personalized treatment plans tailored to the child’s genetic profile can lead to significantly improved outcomes!
How? Let’s find out!
Genetics play a big role in shaping who a child becomes—traits like temperament, personality, and even their risk for mental health challenges. But did you know it’s not just about genes alone?
There’s also epigenetics, which controls how genes are expressed without changing the actual DNA, and this is where both nature (genes) and nurture (environment) come together. The way these factors interact can help us better understand each child’s unique needs.
How does this help? Through genomic profiling, we can now analyze a child’s genetic makeup to get insights into their behavior, tendencies, and even mental health risks. And by identifying specific genetic markers, we can design personalized interventions that target areas where your child might need the most support.
Isn’t it amazing? Understanding these genetic influences means we can create therapies tailored just to your child’s unique needs.
ABA Therapy: A Proven, Evidence-Based Approach
One of the most widely recognized and effective treatments for autism is Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy. ABA focuses on improving specific behaviors, such as social skills, communication, reading, and adaptive learning skills, like dressing, grooming, and hygiene.
How does ABA work? ABA is based on understanding how behavior works in real-life situations. It’s a goal-oriented therapy where therapists work closely with children to break down tasks into smaller, manageable steps. Over time, children learn these behaviors through repetition and positive reinforcement.
Research consistently shows the positive impact of ABA on children with autism. A study published in 2022 found that children receiving early, intensive ABA therapy showed significant improvements in intellectual and social functioning. ABA is considered a gold standard for autism therapy. With the help of genetic testing, ABA programs can be even more personalized to address the specific needs of your child, leading to even better outcomes.
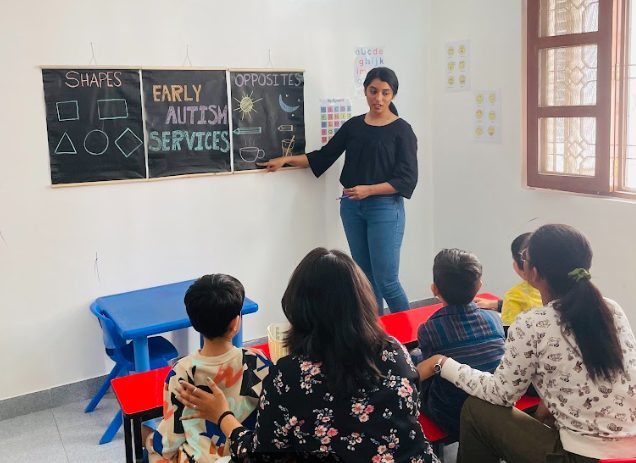
Early Autism Ventures (EAV): A Comprehensive Approach to Autism Support
At Early Autism Ventures (EAV), we go beyond just genetic testing and different therapies. Here’s where we ask the real questions – is your child getting the personalized, comprehensive care they need?
While genetic testing and ABA therapy are crucial, Early Autism Ventures (EAV) takes a comprehensive approach to early autism intervention. We offer a range of services tailored to each child’s unique needs, and our programs incorporate cutting-edge therapies and interventions to ensure that your child receives the best care.
Our mission is to help children with autism reach their fullest potential. By using the latest in genetic research and personalized therapies like ABA, we work with families to create an environment where children can thrive.
But why choose EAV?
- Personalized Treatment Plans: We believe in the power of individualized care. EAV creates therapy plans specifically designed to meet the unique needs of your child.
- Early Intervention: Early intervention is key. The earlier your child starts receiving support, the better the long-term outcomes. Research shows that children who begin therapy before the age of 5 experience significant improvements in communication, social skills, and behavior.
- Family-Centered Approach: At EAV, we work closely with families. We believe that parents and caregivers play an essential role in a child’s therapy. Our goal is to empower you with the tools and resources needed to support your child at home. Read more about the effectiveness of Parent-Child Interaction Therapy (PCIT) here.
- Expert Team: Our team of experts includes experienced ABA therapists, behavioral specialists, and researchers who are passionate about helping children with autism succeed.
How Can EAV Help Your Child?
Autism research continues to evolve. Genetic testing offers promising insights, but it’s just one piece of the puzzle. By combining genetic information with early, intensive behavioral interventions like ABA, families can provide their children with the tools they need to lead happy, fulfilling lives.
At Early Autism Ventures, we understand that every child is different. That’s why we focus on creating tailored, flexible care plans that can adapt as your child grows and develops. We work closely with families to ensure they are fully equipped with the knowledge and support they need.
Our holistic approach integrates genetic testing insights with evidence-based therapies like ABA to create a supportive, nurturing environment for your child to thrive.
Ready to Take the Next Step?
If you’re looking for a comprehensive, personalized approach to autism care, Early Autism Ventures is here to help. Our team is ready to work with you to create a treatment plan that will meet your child’s unique needs.
Contact us today to schedule a consultation and learn more about how we can support your family. Let’s work together to help your child thrive! Schedule a FREE consultation with our clinician now.












Recent Comments